Phesolver
Interactive parallel heat-exchanger flow distribution solver
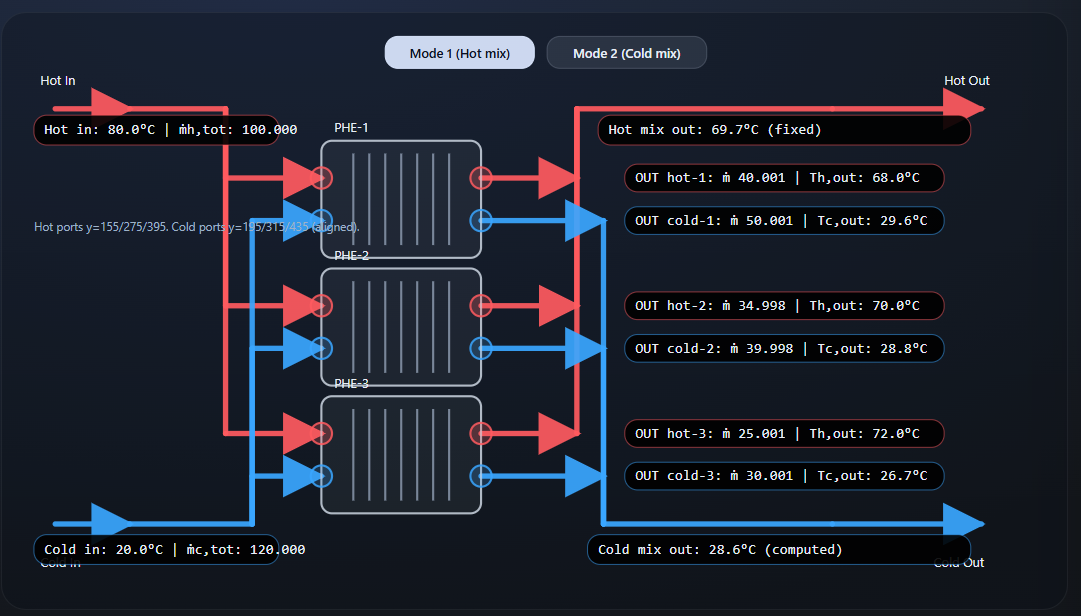
This application is an interactive engineering tool for analyzing three plate-and-frame heat exchangers operating in parallel on a common hot and cold header. Its main purpose is to estimate the flow distribution in each exchanger branch using measured temperatures and total flow rates, while remaining faithful to first-principles energy balances.
Physical model and theory
The model assumes steady-state operation, negligible heat losses, and constant specific heat capacities on both hot and cold sides. For each exchanger branch, an energy balance relates the hot-side temperature drop to the cold-side temperature rise. The total hot and cold flow rates are conserved across the parallel network, and an additional constraint is provided by a measured mixed outlet temperature on either the hot side or the cold side.
The system is solved exactly using:
Three branch energy balances
Two total flow constraints (hot and cold)
One mixing constraint at the combined outlet
This results in a determined linear system that yields the branch-wise hot and cold mass flow rates. Negative or non-physical flows indicate inconsistent measurements rather than numerical failure, making the tool useful for diagnostics as well as calculation.
Two operating modes
The application supports two physically equivalent but diagnostically different modes:
Mode 1 – Hot mixed outlet fixed
The combined hot outlet temperature is treated as a measured, fixed value. The solver adjusts the branch flow rates so that the weighted average of the hot branch outlet temperatures matches this measurement. The combined cold outlet temperature is computed as a result.
Mode 2 – Cold mixed outlet fixed
The combined cold outlet temperature is treated as the fixed measurement. The solver uses the cold-side mixing constraint, and the combined hot outlet temperature becomes a computed result.
Switching modes does not change the physical system; it only changes which mixed outlet temperature is trusted as the closing constraint. Differences in results between modes highlight measurement bias, poor mixing, or modeling assumptions.
Interface and interaction
The schematic shows the full hot and cold piping network with three parallel exchangers. All major temperatures and flows are displayed directly on the diagram, and every label is interactive. Clicking on a label opens an in-place editor, allowing values to be changed directly on the schematic. Any change immediately triggers a re-solve.
A side panel provides structured numeric input fields, mode selection, and presets. Inputs entered in the panel and edits made on the schematic are fully synchronized. Fixed values in the active mode are clearly indicated, while computed values are locked to prevent accidental editing.
Purpose and use
This app is designed as a visual, engineering-grade calculation aid, not a black-box simulator. It helps engineers:
Estimate unknown flow splits in parallel heat exchangers
Validate temperature and flow measurements
Diagnose inconsistent or unrealistic data
Understand how mixing constraints affect inferred flow distribution
The emphasis is on transparency, physical consistency, and immediate visual feedback rather than on complex correlations or detailed exchanger design.